Glorious journey of Indian ISRO – One of the best Space Organizations after NASA
History
ISRO was earlier known as INCOSPAR. After Indian Independence, Indian economy was low. Dr.Vikram Sarabhai ( who is considered as Father of India’s Space Program) took an initiative and came up with the notion of a space program for India.

Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launch Station(TERLS) in kerala , now called as Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC)
1962 – Indian National Committee for Space Research set up by the Department of Atomic Energy. Work starts on Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) in Kerala.
1963 -First sounding rocket launched from TERLS Nov 21.
1965 – Space Science and Technology Center set up in Thumba.
1968 – Experimental Satellite Communication Earth Station set up in Ahmedabad,Gujarat.
Evolution of ISRO

The establishment of the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) was one of his greatest achievements. Dr.Vikram Sarabhai (first chairman of INCOSPAR, which would later be called ISRO) successfully convinced the government of the importance of a space programme for a developing country like India after the Russian Sputnik launch. Dr. Sarabhai emphasized the importance of a space program in his quote:

Dr.Vikram Sarabhai emphasized the importance of a space program in his quote
1969 – Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) formed Aug 15 under the Department of Atomic Energy.
1971 – Satish Dhawan Space Centre (formerly SHAR Centre) formed in Sriharikota, AndhraPradesh.
1972 – Department of Space (DoS) established and ISRO brought under it. It set up in Bangalore and Space Applications Centre in Ahmedabad.
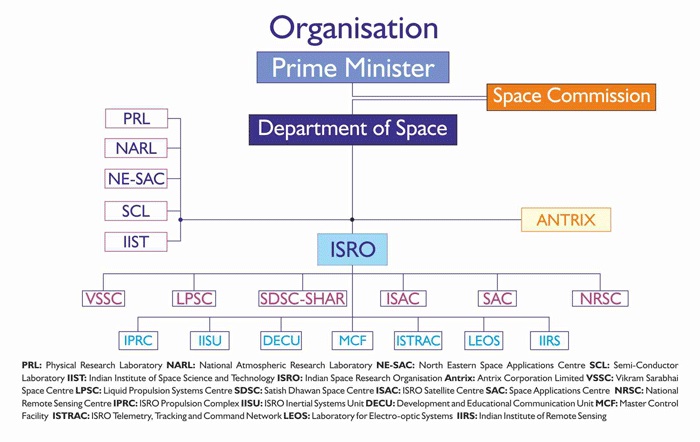
Department of Space(India) organization chart
ISRO achievements
In 1975

Aryabhata, India’s first indigenously built satellite
ISRO launched the first Indian satellite ‘Aryabhata’, named after the 5th Century Indian mathematician and astronomer, using a Russian rocket under then SovietRussia’s international space program ‘Interkosmos’.In the same year, ISRO also started Satellite Instructional Television Experiment (SITE) using American technology which was to bring about a breakthrough in television broadcasting in India. SITE helped television broadcasting to rural India, and marked the arrival of an application-oriented approach to space research.
In 1981

Dr.Abdul kalam teaching at ISRO
ISRO successfully launched satellite Rohini (RS1) into the Earth’s orbit using the very first Indian rocket, the Satellite Launch Vehicle-3 (SLV-3). With this, India became the sixth nation ever to join the exclusive space travels club.A.P.J. Abdum Kalam Ji was the director of the project.
In 1993
ISRO launched a developmental flight of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle( PSLV), an indigenous rocket launcher, which would go on to become the star rocket launcher in Indian space research, despite failure at first launch. (The PSLV followed the Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle programme of the late 80s)
In 2001
The heavy rocket Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) was successfully launched with GSAT-1 satellite. It is designed to place satellites in the Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO).
In 2008

ISRO launched its first mission to the moon using the the spacecraft ‘Chandrayaan’, which was launched using PSLV-XL rocket.The Moon Impact Probe (MIP) crash-landed on the lunar surface on 14 November 2008,The MIP separated from Chandrayaan at 100 km from lunar surface .As it fell, it kept sending information back to the mother satellite which, in turn, beamed the information back to Earth. After scientific analyses of the received data from the MIP, the Indian Space Research Organisation confirmed the presence of water in the lunar soil.It discovered a large number of water molecules on the lunar surface, one of its biggest achievements.
In 2013
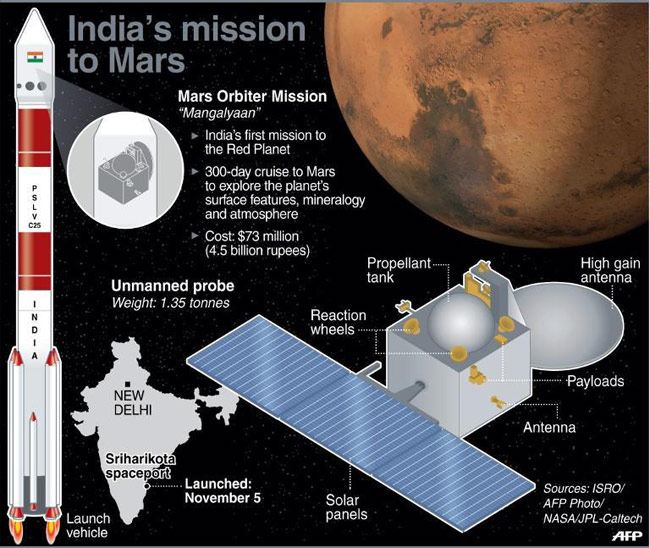
It is the one of the top mission excited by ISRO. The Mangalyaan or Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) was launched on 5th November 2013. ISRO became the first agency to reach Mars in its first attempt. ISRO’s Mars mission is the cheapest so far, just 450 crore i.e Rs 12 per km, equivalent to Auto fare.It reached Mars at a smaller budget than a Hollywood movie.
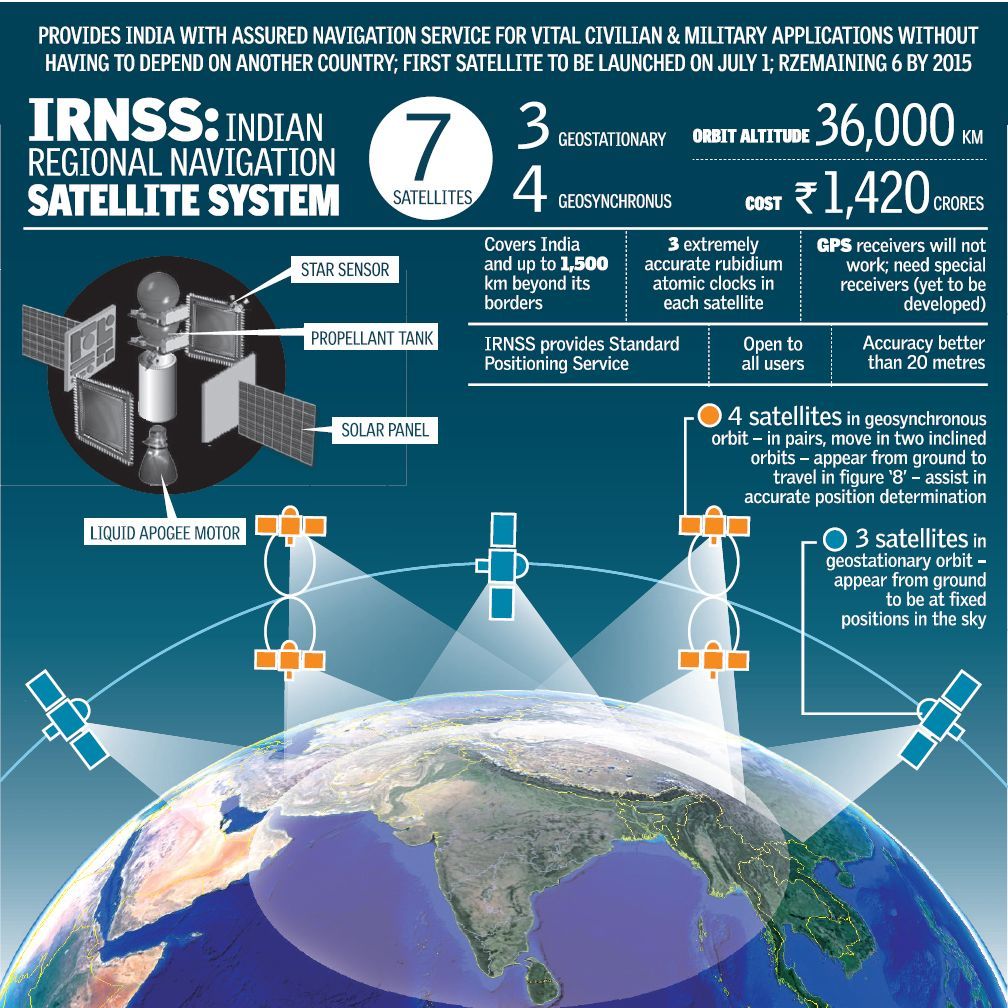
The Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System, with an operational name of NAVIC, is an autonomous regional satellite navigation system that provides accurate real-time positioning and timing services. It covers India and a region extending 1,500km around it, with plans for further extension.The system was developed partly because access to foreign government-controlled global navigation satellite systems is not guaranteed in hostile situations, as happened to the Indian military in 1999 when it was dependent on the American Global Positioning System (GPS) during the Kargil War. The Indian government approved the project in May 2006.
In 2017

ISRO launches record 104 satellites at Sriharikota,AndhraPradesh.
India Space Research Organisation (ISRO) scripted history by launching 104 satellites (overtaking the previous record of 37 satellites launched by Russia in 2014) on the aptly titled ‘workhorse’ of Indian space travels, the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle rocket, from the Sriharikota station in Andhra Pradesh.This is the highest number of satellites that have ever been launched into space in a single mission by any institution in the world.
ISRO vs NASA

We all know that NASA is the space agency of United States of America, one of the richest and developed countries in the world. ISRO is the space agency of the India which is a developing country, so the difference in budget and costly technologies will reflect in the performance of both agencies.
The moto of both the agencies is totally different
NASA → “To reach for new heights and reveal the unknown so that what we do and learn will benefit all humankind”
ISRO → “Our vision is to harness space technology for national development, while pursuing space science research and planetary exploration”
NASA doesn’t even have a single space vehicle for its transportation. Although, Orion is still in its infantry stage it didn’t qualify for implementation.
ISRO was founded in the year when Neil armstrong first set his foot on the moon. So,this itself says the technological gap between the 2 agencies.
Given the time limit and success rate for any mission, I think, ISRO always tops the list. With its workhorse PSLV(Polar satellite launch vehicle) the success rate is estimated to be 93%. And this is considered to be one of the most reliable mode of transport of satellites.
1. Launching Vehicles
ISRO’s first rocket was launched in 21st November 1963 was imported from Russia. At that time India doesn’t have a space agency. After 6 years in August 15th 1969 ISRO was formed. After that it developed a series of launch vehicles like SLV, ASLV, PSLV, GSLV and its different variants and conducted many satellite launches.Using these vehicles ISRO launched a lot of satellites for indigenous use and also as a part of the agreement with different space agencies.
In the USA the scenario is different Most of the rockets used by NASA are developed by joint venture between NASA and other private companies. Except for some old rockets likeAtlas-Agena, Thor-Ablestar, Thor-Delta, SM-65E Atlas.The Recent satellite launches NASA used SPACE X rockets.
2.Commercial Satellite Launches and Mission Budgets
In commercial satellite launches, ISRO has the upper hand in the world. ISRO’s commercial satellite launches are conducted by Antrix Corporation Limited.
ISRO launched 104 satellites in a single launch.While comparing ISRO vs NASA,the US space agency is far behind in this achievement.The other thing in which ISRO has the upper hand is in executing low-cost space missions. Indian Mars mission MOM is the world’s cheapest Mars mission. This capability of ISRO makes attract world countries to approach ISRO for their satellite launches.India’s mars mission costed about 69 million dollars and took about 18 months of preparation compared to 5 years and about 670 million dollars took by NASA for their mars mission.
On similar lines India’s mission to moon took about 59 million dollars which is about 10% of NASA’s budget for its similar mission to moon.the total annual budget for (NASA → 1218.34 billion) & (ISRO → 90.94 billion).The difference in funds is obvious.
These facts about ISRO vs NASA shows a result that both space agencies have their unique role in lifting humankind in new heights. ISRO and NASA have long diversity in their socio-economic background that will reflect in the missions they plan.
Upcoming launch
ISRO’s GSAT-29 launch is in October,another launch is planned involving a PSLV during which 30 commercial satellites would be launched.
For more updates
click here: Interesting Facts and Updates
[…] for more info click : http://weindianseverywhere.co.in/glorious-journey-of-indian-isro-one-of-the-best-space-organizations… […]